How Does a Generator Work? | Working Principle of Small Generators
(Basic Principle)
Generators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction. When a conductor cuts magnetic flux lines in a magnetic field, an electromotive force (voltage) is generated, producing electric current.
二、(Key Components)
1. (Engine)
- Provides mechanical power, usually fueled by gasoline, diesel, or propane.
2. (Rotor & Stator)
- *Rotor*: Rotating magnets or electromagnets to generate a magnetic field.
- *Stator*: Fixed coils that cut the magnetic field to produce current.

3. (Voltage Regulator)
- Stabilizes output voltage to protect connected devices.
4. (Cooling & Exhaust)
- Prevents overheating for prolonged operation.
三、(Working Process)
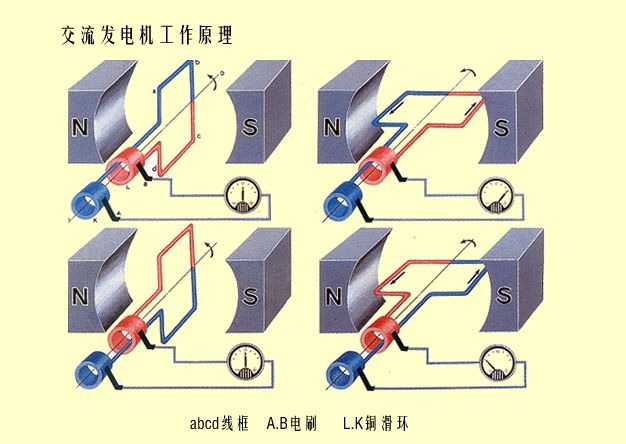
*Start the engine* → Rotates the rotor → Creates a rotating magnetic field.
2. AC)。
*Stator coils cut the field* → Generates alternating current (AC).
3. (DC)。
*Via a rectifier (if needed)* → Converts to direct current (DC).
4. *Voltage regulator controls* → Delivers stable voltage (e.g., 220V/50Hz or 110V/60Hz).
四、(Advantages of Small Generators)
*Portable design for home, camping, or emergency use.*
*Low noise and high efficiency.*
*Multi-fuel options (gasoline/diesel/dual-fuel).*
五、(Maintenance Tips)
*Regularly change oil and air filters.*
*Avoid overloading.*
*Drain fuel if storing long-term.*
Last : Six Essential Tips for Proper Use of Small Gasoline Generators
Next: Gasoline vs Diesel Generators: How to Choose the Right Model?
Message